Have you ever thought of the difference between a prefab and a modular home? They both sound modern, efficient, and faster than traditional builds but do they really mean the same thing? Well, The truth is, there are crucial differences that can impact your costs, scheduling, and even design decisions.
In this article, we will discuss 6 unexpected differences between prefab and modular homes and help you decide which one is best for you. So keep reading!
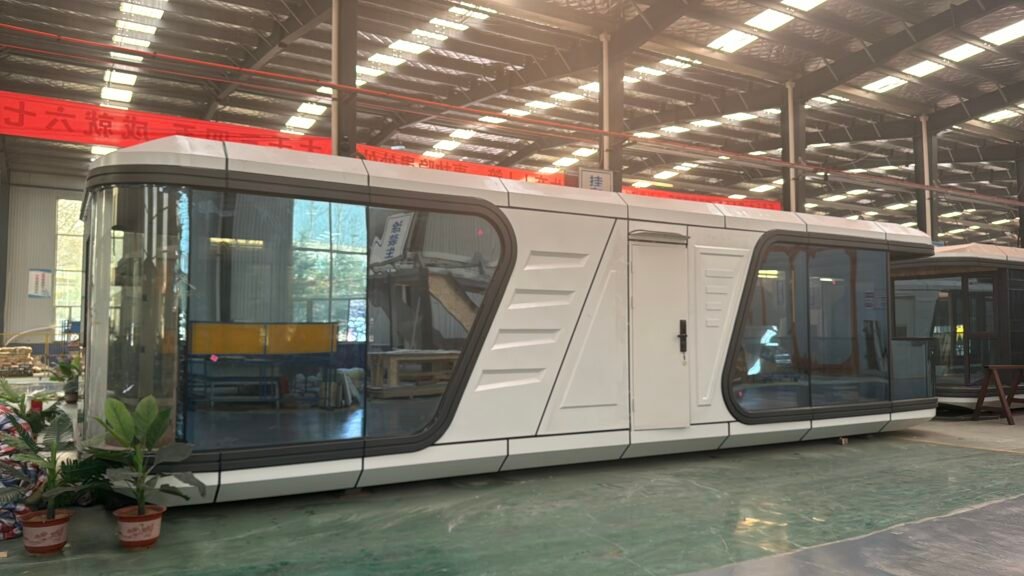

1) The Balance Between Factory Pre-assembly and Field Work
A major distinction between prefab and modular houses is the location of construction work.
i) Prefab house
Just like with standard home construction, prefab houses require some work to be done outdoors. Prefab homes are built by constructing flat wall panels and roof sections, which are then shipped to the location. A construction team is dispatched, which then assembles the pieces on site.
ii) Modular home
Modular homes are unique as well and different from traditional home construction. The initial step consists of building modules or large blocks which resemble rooms in a factory. A staggering 80% to 95% of the home is finalized before it leaves the factory for the last touch which is stacking, sealing gaps, and connecting water, electricity, and gas systems in the house.

2) Building Codes and Inspection Requirements
Another difference is the guidelines the houses have to comply with and the methods used to verify their safety.
Prefab homes: These homes may have different regulations that are not local, for instance:
- Some people work under an industrialized building code. These standards are more flexible and may not be aligned with the regulations of your municipality.
- Some, such as built HUD-codes manufactured homes, adhere to broad regulations set by the federal government. While these regulations are acceptable for safety considerations, they may not be as thorough as your local or state regulations.

Modular homes: Just like a traditional house built on-site, modular homes have to comply with all building codes. These building codes come from your city and state. They ensure that the house is safe, structurally sound, and livable.
Even better, modular homes are inspected twice. First, as everything is constructed in a factory, an inspector checks everything. Then, another inspection occurs once the home is placed on the owner’s lot and set up. This means modular homes tend to be quite safe and dependable.
3) Transport and Setting in Place
Now we will discuss the movement and installation of prefab and modular homes on your land.
Prefab homes: Just like the delivery of cars and their parts, houses, too, are constructed like puzzles that need to be fitted together part by part. A house begins its journey in the form of segments, such as wall panels or roof parts. These segments are loaded onto standard flatbed trucks and transported similarly to how one would transport a car.
These trucks are used for all sorts of large shipment. When these flatbed trucks reach your desired location, there is always a team of workers called framing crews that assemble the pieces so that the house is ready to live in. The house is not fully ready, it needs the finishing touches.
These finishing touches need to be done after the parts are fitted so that they do not get damaged while assembling the house. Similar to constructing with a large set of blocks, this requires more effort and time.

Modular homes: In contrast, modular homes are made of big box-shaped objects called modules. These are transported with special heavy-load bearing trucks. A big crane lifts each module and places it on the house’s foundation. This is usually done within one day.
4) Custom Design Flexibility
Prefab homes: With prefab homes, you can easily access any style you want. Whether it’s modern, farmhouse, or other fancier designs, prefab systems can be tailored as needed. But there’s a downside to unique shapes or designs; the extra work required expands at the building site.
This means possibly more time, additional employees, and in some cases, an increase in expenses.
Modular homes: Every part of modular homes is constructed in a boxed section, where each section precisely fits on a truck. Because of this, modular designs conform to a grid order, like blocks that snap together.
While color choices and finishes allow for open customization, design elements like strong open areas, atypical roof outlines, or vaulted ceilings might pose challenges. Due to additional engineering requirements, special features often need more steel, making the home more costly.

5) Cost and Construction Timeline
Prefab and modular homes differ in construction methods as well as cost and timeframe. Here we will discuss the comparison in the table:
Stage | Prefab Panels | Modular Boxes |
Factory Lead Time | 2–4 weeks | 6–8 weeks |
On-Site Build Time | 3–6 months | 4–8 weeks |
Typical Cost/ft² | $150–$250 | $180–$300 |
Key Takeaway | Cheaper if local labor is available | Saves money by reducing on-site time |
6) Financing, Resale, and Long-Term Value
Usually, when purchasing a house, it requires a loan, and selling it later on is also an option. Prefabricated and modular homes have a different approach to both selling and buying.

- Prefab homes: There’s a chance prefab homes are a bit different. In some cases, you might need something known as a construction-to-permanent loan. This is where the loan is in place during the construction phase and transforms into a standard loan once the building is finished.
In addition, selling prefab homes highly depends on public perception of them. Some regions might be open to it, while others may not.
- Modular homes: Just like traditional homes, modular houses are treated equally. Consistent with this, banks offer a regular mortgage loan, also known as a conventional mortgage. Moreover, the resale value associated with these homes is significant as they are constructed similar to site-built houses.
7) Pros and Cons of Prefab vs. Modular Homes
Like any other structure, prefab and modular homes have their advantages and disadvantages. Now we will discuss an overview of the most notable pros and cons of each to help you make an informed decision on which one would be best suited for you:
Category | Prefab Homes | Modular Homes |
Design Flexibility | More design options and styles | Limited by module sizes and shapes |
Build Speed | Longer on-site build time | Faster overall build and installation |
Building Codes & Quality | May follow looser codes, less factory control | Built to strict local codes, high factory quality |
Cost | Usually cheaper if local labor is available | Slightly higher cost per square foot |
On-Site Work Required | More on-site labor needed | Minimal on-site work after delivery |
Financing Options | May need special construction loans | Qualifies for regular mortgages |
Resale Value | Depends on local market acceptance | Appraises like site-built homes |
Disha Bangera from Quora explained that many people confuse modular homes with prefabricated homes, but they are not exactly the same. Prefab homes are built in parts at a factory, which makes them faster to construct and more eco-friendly.
She mentioned that prefab designs can look like modular homes, and thanks to companies like Champion Prefabs, more people can now own stylish and functional prefab houses. She also suggested talking to construction companies for better clarity and guidance.
Conclusion
In the end, both prefab and modular houses are contemporary and smart building methods. Prefab homes offer greater flexibility in design but require more onsite work. In contrast, modular homes are quicker to complete and more strictly governed by construction codes.
So, knowing the important differences helps you select the best home for your future according to your budget, schedule, and design objectives. Moreover, we provide at Glamni modular houses that are thoughtfully designed and constructed to meet your specific needs. Reach out to us today at Glamni, We would love to help you!


